Attrition Rate
Attrition rate refers to the rate at which employees leave a company over a specific period of time, usually expressed as a percentage of the total workforce. This can include employees who resign voluntarily, retire, or are terminated by the company.
The attrition rate represents the ebb and flow of individuals within a company — those who leave, and those who join —quantifying a dynamic aspect of organizational health.
Understanding attrition rate goes beyond numbers; it's a narrative of employee and customer relations, reflecting satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty. In this comprehensive guide, we aim to demystify the intricacies behind attrition, shedding light on why it matters and how it influences an organization's vitality.
Join us as we delve into what is attrition rate, seeking to understand, adapt, and cultivate a sustainable future for your organization.
What is the attrition rate?
The attrition rate means the rate at which employees leave a company over a specific period, usually expressed as a percentage of the total workforce. This can include employees who resign voluntarily, retire or are terminated by the company.
A high attrition rate can indicate a number of underlying issues, such as poor job satisfaction, lack of career development opportunities, or inadequate compensation and benefits. It can also be a costly affair for employers, as they may need to invest resources into recruiting and training new employees to fill the positions left by departing employees.
Employers may track attrition rates to monitor employee turnover and identify patterns or trends. They may also use this data to develop strategies to reduce attrition and retain valuable employees, such as improving employee engagement, offering competitive compensation and benefits, and providing opportunities for career development and advancement. A low attrition rate can be a positive indicator of a healthy and stable workforce.
You may like: What is a Healthy Attrition Rate?
Why are attrition rates important?
Attrition rates are important because they can provide insights into employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity. A high attrition rate can be a sign that employees are not happy with their jobs, the company culture, or the compensation and benefits package.
This can lead to a number of negative consequences, including:
- Decreased productivity
- Increased costs associated with hiring and training new employees
- A decline in morale among the remaining employees
- Damage to the company's reputation
- Difficulty attracting and retaining top talent
By tracking their attrition rates over time, businesses can identify trends and patterns that can help them identify areas where they need to focus their efforts in order to reduce attrition.
For example, if a company finds that they have a high attrition rate among new hires, they may need to improve their onboarding and training process. If a company finds that they have a high attrition rate among women or minorities, they may need to implement diversity and inclusion initiatives.
How to calculate attrition rate?
Calculating employee attrition rate involves determining the percentage of employees who leave a company within a specific period.
The formula for calculating the attrition rate is:

Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
- Define the time: Decide on the time period for which you want to calculate the attrition rate (e.g., monthly, quarterly, or annually).
- Determine the Number of Employees Who Left: Count the number of employees who left the company during the chosen time period.
- Determine the Average Number of Employees: Calculate the average number of employees during the same time period. This is usually done by adding the number of employees at the beginning and end of the period, then dividing by 2.

- Use the Formula: Apply the formula mentioned above to find the attrition rate.
Attrition Rate = Number of Employees Who LeftAverage Number of Employees during the period100
- Multiply by 100: Multiply the result by 100 to express the attrition rate as a percentage.
For example, if 15 employees left during the quarter, and the average number of employees during that quarter was 500:
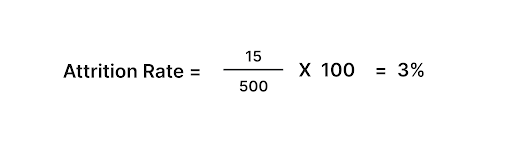
So, the attrition rate for that quarter would be 3%. This metric can provide valuable insights into employee turnover and retention strategies within an organization.
You may like: How To Calculate Attrition Rate In Excel?
Employee Attrition Rate Formula
The formula to calculate the employee attrition rate is:
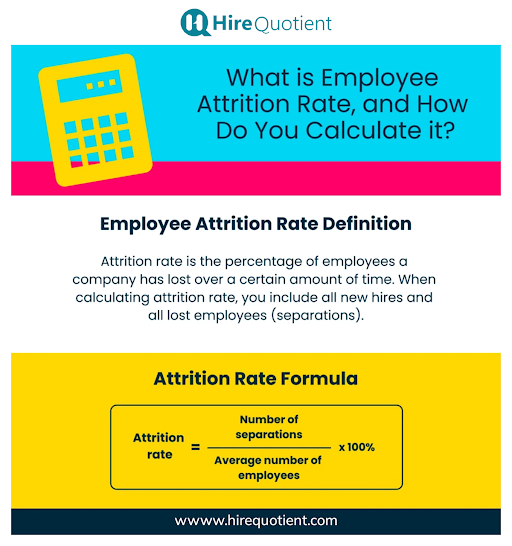
Here's a breakdown of the variables:
- Number of Employees Who Left: This is the total count of employees who left the organization during a specific time period (e.g., a month, quarter, or year).
- Average Number of Employees During the Period: Calculate the average number of employees in the organization during the same time period. This is usually computed by adding the number of employees at the start and end of the period and dividing by 2.
- Multiply by 100: To express the attrition rate as a percentage, multiply the result by 100.
Putting it all together, the formula provides a percentage that represents the proportion of employees who left compared to the average number of employees during the specified time frame.
You may like: What is a Bad Attrition Rate?
Pros and Cons of Understanding Attrition Rate
Pros of Understanding Attrition Rate
- Identifying Problem Areas:
Pro: Attrition rates help identify departments or teams with high turnover, indicating potential issues that need attention.
- Strategic Workforce Planning:
Pro: Organizations can plan for staffing needs and talent acquisition more strategically by understanding historical attrition patterns.
- Cost Management:
Pro: Knowing the attrition rate allows organizations to estimate and manage recruitment and training costs associated with employee turnover.
- Employee Engagement Insights:
Pro: Attrition data can provide insights into employee satisfaction and engagement levels, helping organizations address underlying issues.
- Improving Retention Strategies:
Pro: With a clear understanding of attrition reasons, organizations can implement targeted retention strategies to enhance employee loyalty.
- Competitive Benchmarking:
Pro: Comparing attrition rates with industry benchmarks helps organizations gauge their competitiveness in retaining talent.
- Enhanced Organizational Health:
Pro: A low attrition rate is often indicative of a healthy organizational culture and positive work environment.
You may like: What is a Good Attrition Rate?
Cons of Understanding Attrition Rate
- Sole Metric Limitations:
Con: Relying solely on attrition rates may not provide a complete picture of workforce dynamics, as it doesn't account for the quality or performance of replacements.
- Overemphasis on Short-Term Data:
Con: Focusing too much on short-term attrition rates may lead to overlooking broader workforce trends or industry shifts.
- Complex Causes:
Con: Attrition rates might not capture the complex and multifaceted reasons behind employee departures, such as personal factors or career changes.
- Potential for Misinterpretation:
Con: Misinterpreting attrition data can lead to misguided interventions, as not all turnover is necessarily negative.
- Not Accounting for Employee Movements:
Con: Attrition rates may not distinguish between voluntary resignations, retirements, and internal promotions or transfers.
- Influence of External Factors:
Con: Economic conditions, industry trends, or global events can influence attrition rates, making it challenging to attribute changes solely to internal factors.
- Negative Organizational Perception:
Con: A high attrition rate may create a negative perception of the organization among potential employees, clients, or investors.
What are the different types of Attrition Rates?
Attrition rates can be categorized into different types based on the specific focus or characteristics of the departures being measured.
Here are some common types of attrition rates:
- Employee Attrition Rate: Measures the percentage of employees who leave an organization over a given period.
- Voluntary Attrition Rate: Focuses on the percentage of employees who voluntarily resign or leave the organization, often indicating dissatisfaction or personal decisions.
- Involuntary Attrition Rate: Calculates the percentage of employees who are involuntarily terminated or laid off by the organization.
- Internal Movements Rate: Examines the percentage of employees who leave their current positions but remain within the organization through transfers or promotions.
- External Movements Rate: Tracks the percentage of employees who leave the organization, including those who resign, retire, or move to other companies.
Read more about types of Attrition:
- What Is Natural Attrition?
- What is Regretted Attrition?
- What is Unregretted Attrition?
- What Is Regrettable Attrition?
- What is Differential Attrition?
What is a Good Attrition Rate?
A good attrition rate will vary depending on the industry, company size, and other factors. However, a generally accepted rule of thumb is that an attrition rate of 10% or lower is considered healthy. This means 10% or fewer employees are leaving the company each year.
An attrition rate of over 10% may be a sign that the company is experiencing problems with employee engagement, retention, or culture. This can lead to a number of negative consequences, including reduced productivity, increased costs, and a decline in morale.
What is a high attrition rate?
A high attrition rate is typically considered to be significantly above the industry average or the historical norms for a specific organization. While there is no universal threshold, if the attrition rate is consistently higher than comparable companies or the organization's own historical data, it may be deemed high. It becomes a concern when the rate adversely impacts operational efficiency, increases recruitment costs, and signals potential issues with employee satisfaction and engagement.
You may like: Top 7 Tips for Managing Employee Attrition
What causes high attrition rates?
There are a number of factors that can contribute to high attrition rates, including:
- Low pay and benefits: Employees who are not paid fairly or who do not have access to competitive benefits are more likely to leave their jobs.
- Lack of opportunities for advancement: Employees who do not see opportunities for advancement within their company are more likely to look for jobs elsewhere.
- Poor work-life balance: Employees who have difficulty maintaining a healthy work-life balance are more likely to leave their jobs.
- Toxic work environment: Employees who work in a toxic or negative work environment are more likely to leave their jobs.
- Performance issues: Employees who are struggling to perform their jobs are more likely to be terminated.
- Misconduct: Employees who engage in misconduct, such as theft or harassment, are more likely to be terminated.
- Layoffs: Layoffs are a type of involuntary attrition that can occur when a company needs to reduce its workforce.
How can you reduce high attrition rates?
Reducing high attrition rates requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying causes of employee departures and the factors that contribute to a positive and engaging workplace. Here are strategies to help mitigate high attrition rates:
- Conduct Exit Interviews: Gather feedback from departing employees through exit interviews to understand the reasons behind their decision to leave. Use this information to identify patterns and address root causes.
- Improve Leadership and Management Practices: Invest in leadership development programs to enhance management skills. Ensure that leaders communicate effectively, provide clear expectations, and foster a positive work environment.
- Offer Competitive Compensation and Benefits: Regularly review and benchmark salaries and benefits to ensure they are competitive within the industry. Consider additional perks or incentives to attract and retain talent.
- Provide Career Growth Opportunities: Implement career development programs, mentorship initiatives, and pathways for advancement within the organization. Communicate clearly about growth opportunities to motivate employees to stay.
- Enhance Work-Life Balance: Encourage a healthy work-life balance by promoting flexible work arrangements, setting realistic workload expectations, and discouraging excessive overtime.
- Cultivate a Positive Organizational Culture: Foster a positive workplace culture that values diversity, inclusivity, and employee well-being. Recognize and celebrate achievements, and address toxic behaviors promptly.
Attrition Rate vs Turnover Rate
| Aspect | Attrition Rate | Turnover Rate |
| Definition | The natural reduction in the size of the workforce over time, including both voluntary and involuntary departures. | Specifically refers to the number or percentage of employees who voluntarily leave the organization. |
| Scope | Encompasses both voluntary and involuntary departures, including retirements, resignations, and terminations. | Focuses on voluntary departures, such as resignations, and excludes involuntary separations like terminations or retirements. |
| Calculation | Calculated as the percentage of employees who leave the organization (voluntarily or involuntarily) within a specified period. | Calculated as the percentage of employees who voluntarily leave the organization within a specified period. |
| Consideration | Provides a broader view of overall workforce movement, including both planned and unplanned departures. | Specifically addresses the voluntary aspect of employee turnover, often reflecting employee satisfaction and engagement. |
| Use Cases | Commonly used when analyzing the overall health of the workforce, including retirements and planned exits. | Often used to assess the impact of voluntary departures on organizational stability and employee retention strategies. |
Is employee attrition always bad?
Employee attrition is not inherently "bad" or "good." Whether it is considered positive or negative depends on the circumstances surrounding the departures and the overall impact on the organization. Here are some perspectives to consider:
Positive Aspects of Employee Attrition
- Natural Workforce Evolution: Attrition is a natural part of workforce evolution. It allows for the infusion of new talent, skills, and perspectives into the organization.
- Opportunities for Growth: Attrition creates opportunities for internal promotions and career advancement for existing employees, contributing to their professional development.
- Addressing Performance Issues: In some cases, attrition can help remove underperforming employees, leading to a more productive and motivated workforce.
- Adjustment to Market Changes: Attrition allows organizations to adapt to changes in the market or industry by reshaping their workforce to meet evolving needs.
Negative Aspects of Employee Attrition:
- Loss of Knowledge and Expertise: High attrition can lead to a loss of institutional knowledge and expertise, especially if experienced employees leave without adequate knowledge transfer.
- Disruption in Team Dynamics: Frequent departures can disrupt team dynamics, affecting collaboration and productivity.
- Recruitment and Training Costs: High attrition rates can increase recruitment and training costs, as the organization invests resources in replacing and onboarding new employees.
- Impact on Morale: Persistent attrition may negatively impact employee morale, leading to a sense of instability and reduced engagement.
Employee attrition analysis
Employee attrition analysis is the process of collecting and analyzing data to identify the factors that contribute to employee turnover. This information can then be used to develop strategies to reduce attrition and improve employee retention.
There are a number of different ways to conduct employee attrition analysis. One common approach is to use exit surveys to gather feedback from departing employees. Exit surveys can ask employees about their reasons for leaving, their satisfaction with the job and the company, and any suggestions they have for improvement.
Another approach to employee attrition analysis is to use data from human resources systems to track employee turnover rates and identify trends. This data can be used to identify which departments or job roles have the highest attrition rates, as well as which employee demographics are most likely to leave the company.
Once the data has been collected, it is important to analyze it carefully to identify the root causes of attrition. This may involve looking for correlations between different factors, such as job satisfaction, salary, and turnover rates.
Once the root causes of attrition have been identified, businesses can develop strategies to address them. For example, if a company finds that employees are leaving because they are not satisfied with their salaries, the company may need to offer more competitive salaries. If a company finds that employees are leaving because they do not have opportunities for advancement, the company may need to create more opportunities for employee development.
Here are some tips for conducting employee attrition analysis:
- Collect data from multiple sources. This will give you a more complete picture of the situation.
- Use a variety of analysis methods. This will help you to identify different patterns and trends.
- Look for correlations between different factors. This will help you to identify the root causes of attrition.
- Be transparent with your findings. Share your findings with employees and managers so that they can take action to address the root causes of attrition.
Tips for attrition management
Here are some tips for attrition management:
- Understand the reasons for attrition. The first step to managing attrition is to understand the reasons why employees are leaving. This can be done through exit surveys, focus groups, and one-on-one conversations with departing employees. Once you understand the reasons for attrition, you can start to develop strategies to address them.
- Offer competitive pay and benefits. Employees are more likely to stay with a company if they are paid fairly and have access to competitive benefits. Make sure that your pay and benefits packages are in line with industry standards.
- Provide opportunities for advancement. Employees want to feel like they are growing and learning in their careers. Provide employees with opportunities to develop their skills and knowledge, and to advance to more senior positions.
- Create a positive work environment. Employees want to work in a positive and supportive environment. Create a culture of respect, teamwork, and collaboration.
- Address performance issues early on. If employees are struggling to perform their jobs, it is important to address these issues early on. Provide employees with the support they need to improve their performance. If performance issues are not addressed, employees may be more likely to leave the company.
- Provide regular feedback and training. Employees want to feel valued and appreciated. Provide employees with regular feedback on their performance, and offer them opportunities to develop their skills and knowledge.
- Recognize and reward employees. Employees want to feel like their hard work is appreciated. Recognize and reward employees for their accomplishments, both big and small.
- Make sure employees feel valued and respected. Employees want to feel like they are making a contribution to the company and that their work is appreciated. Managers should regularly communicate with their team members and provide positive feedback.
- Listen to employee feedback and take action on it. Employees want to feel like their voices are being heard. Managers should regularly survey employees and take action on their feedback whenever possible.
- Invest in employee development. Employees want to grow and learn in their careers. Companies should provide employees with opportunities to develop their skills and knowledge.
- Promote work-life balance. Employees want to have a healthy work-life balance. Companies should offer flexible work arrangements and encourage employees to take time off.
Over to You
Organizations are encouraged to adopt a proactive stance toward attrition management. Instead of viewing attrition as an inevitable challenge, consider it as a catalyst for positive change and growth.
Attrition, whether viewed through the lens of departures, transitions, or opportunities, is an inherent facet of organizational life. What sets thriving organizations apart is not the absence of attrition but the wisdom to navigate it proactively. From deciphering the intricacies of attrition rates to the strategic implementation of retention measures, our exploration has underscored the pivotal role that foresight and adaptability play in cultivating a resilient workforce.
Attrition Rate: Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is attrition rate?
Attrition rate, often referred to as turnover rate, measures the number of employees or customers who leave a company over a specific period. It is a critical metric for businesses to understand workforce stability and customer retention.
2. What does attrition rate mean?
The attrition rate indicates the rate at which employees or customers leave an organization and are not replaced. It helps in assessing the overall health and efficiency of a company’s human resources or customer service strategies.
3. How to calculate attrition rate?
To calculate the attrition rate, use the formula:
(Number of Leavers/Average Number of Employees or Customers)×100
This will give you the percentage of attrition over a given period.
4. What is a good attrition rate?
A good attrition rate varies by industry, but generally, a lower rate is better. For many sectors, an annual attrition rate of 10% or lower is considered good, indicating stability and employee or customer satisfaction.
5. What is a high attrition rate?
A high attrition rate typically indicates issues within an organization, such as poor management, lack of career growth, or low employee morale. Rates above 20% are often seen as high and may warrant further investigation and action.
6. How do you calculate employee attrition rate?
To calculate the employee attrition rate, divide the number of employees who left during a period by the average number of employees in that period, then multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
7. How to calculate the customer attrition rate?
The customer attrition rate is calculated by dividing the number of customers lost during a specific period by the number of customers at the start of the period, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
8. What is a good attrition rate for a company?
A good attrition rate for a company generally falls below 10-15%, but this can vary by industry. It reflects a stable workforce and effective retention strategies.
9. What is the employee attrition rate?
Employee attrition rate measures the percentage of employees who leave a company over a specified period and are not replaced. It is a key indicator of employee turnover.
10. How to calculate the annual attrition rate?
To calculate the annual attrition rate, divide the total number of employees who left during the year by the average number of employees for the year, then multiply by 100.
11. How is the attrition rate calculated?
The attrition rate is calculated using the formula: (Number of Leavers/Average Number of Employees or Customers)×100, resulting in a percentage that represents the turnover.
12. What does high attrition rate mean?
A high attrition rate suggests significant turnover, which may be due to dissatisfaction, better opportunities elsewhere, or internal issues such as poor management or work conditions.
13. What is a healthy attrition rate?
A healthy attrition rate varies by industry but generally ranges between 5-10%. This rate indicates a balance where there is enough turnover to bring in new talent while retaining experienced employees.
14. How to calculate voluntary attrition rate?
Voluntary attrition rate is calculated by dividing the number of employees who left voluntarily by the total number of employees at the beginning of the period, then multiplying by 100.
15. What is customer attrition rate?
Customer attrition rate, also known as customer churn rate, measures the percentage of customers who stop doing business with a company over a specific period.
16. What is attrition rate in HR?
In HR, attrition rate refers to the rate at which employees leave the organization and are not replaced. It is a critical metric for workforce planning and strategy.
17. How to calculate employee attrition rate in Excel?
To calculate employee attrition rate in Excel, use the formula (Number of Employees Who Left/Average Number of Employees)×100. Input the numbers into Excel and use cell references for calculation.
18. How to reduce attrition rate?
Reducing attrition rate can be achieved by improving employee satisfaction through better management, career development opportunities, competitive compensation, and a positive work environment.
19. What is a low attrition rate?
A low attrition rate indicates that a small percentage of employees or customers are leaving over a period, which is generally positive as it suggests stability and satisfaction.
20. How to measure attrition rate?
Attrition rate is measured by dividing the number of employees or customers lost over a period by the average number of employees or customers during that period, then multiplying by 100.
21. What is attrition rate in research?
In research, attrition rate refers to the percentage of participants who drop out of a study before it is completed. High attrition rates can affect the validity of the research findings.
22. What is attrition rate in college?
Attrition rate in college measures the percentage of students who leave before completing their degree. This can be an important indicator of the institution’s ability to retain students.
23. What is the average attrition rate in the IT industry?
The average attrition rate in the IT industry varies but is generally higher than in other sectors, often ranging from 15-20%, due to rapid technological changes and high demand for skilled professionals.
24. How to calculate quarterly attrition rate?
To calculate the quarterly attrition rate, divide the number of employees or customers lost during the quarter by the average number of employees or customers for that quarter, then multiply by 100.
25. What is the attrition rate in HR?
Attrition rate in HR refers to the percentage of employees leaving the company over a certain period. It is used to evaluate the effectiveness of HR practices in retaining talent.
26. How to determine attrition rate?
Attrition rate is determined by dividing the number of people who leave a company or organization by the average number of people during the period, then multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage.
27. What is a high attrition rate?
A high attrition rate indicates a high level of turnover within an organization, which can signal underlying problems such as poor management, lack of career growth, or dissatisfaction among employees or customers.
28. How to calculate attrition rate in a research study?
To calculate the attrition rate in a research study, divide the number of participants who dropped out by the total number of participants at the start, then multiply by 100.
29. What is a good attrition rate for a company?
A good attrition rate for a company is typically below 10-15%, suggesting effective retention strategies and a stable workforce.
30. How to figure out attrition rate?
Attrition rate is figured out by using the formula: (Number of Leavers/Average Number of Employees or Customers)×100.
This provides the percentage of turnover.
31. How to calculate the attrition rate?
The attrition rate is calculated by dividing the number of people who left during a period by the average number of people over that period, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
32. What is rate of attrition?
The rate of attrition, also known as turnover rate, measures the percentage of individuals leaving an organization over a specified period.
33. How to calculate the monthly attrition rate?
To calculate the monthly attrition rate, divide the number of employees or customers who left during the month by the average number of employees or customers for that month, then multiply by 100.
34. What does a low attrition rate mean?
A low attrition rate means that a small percentage of employees or customers are leaving over a period, generally indicating satisfaction and stability within the organization.
35. How to calculate the attrition rate in Excel?
To calculate attrition rate in Excel, input the number of leavers and the average number of employees or customers, then use the formula: (Leavers/Average Number)×100.
36. How to calculate attrition rate in research?
In research, attrition rate is calculated by dividing the number of participants who drop out by the total number of participants at the start of the study, then multiplying by 100.
37. What is an acceptable attrition rate?
An acceptable attrition rate varies by industry but is generally considered to be around 10-15%. This rate indicates a healthy level of turnover, allowing for new talent while retaining experienced employees.
38. How would the overall population of each side affect the rate of attrition?
The overall population affects the attrition rate as larger populations may have more significant fluctuations in absolute numbers, while smaller populations might see more dramatic percentage changes with fewer leavers.
39. What is high attrition rate meaning?
A high attrition rate generally means a significant portion of employees or customers are leaving the organization. It often indicates underlying problems such as dissatisfaction, poor working conditions, or better opportunities elsewhere.
40. What is attrition rate definition?
Attrition rate, also known as turnover rate, is defined as the percentage of employees or customers who leave an organization over a specific period.


